An Internet Protocol (IP) address is a combination of numbers that belongs to every device connected to the internet. Each IP address is unique to the device the IP address belongs to. Even devices that are in a local network have one.
Table of Contents
What Does IP Mean?
The term IP refers to the rules that enable the transmission of information in the form of data packets over a given network. All devices connected to the internet have a network interface card.

The network—in this case, the internet—needs to distinguish between two devices. It does this by assigning each device on the network a unique string of numbers, which is the Internet Protocol address. The IP is the method that network devices use to send and receive data on a network from other devices.
How Do IP Addresses Work?
IP addresses work by following a set of guidelines for communication in order to transfer data. An IP address is formed by 32 bits. When a user takes a look at any device’s IP address, it comes in the form of four octets of numbers ranging from 0 to 255. Depending on this number, the IP address can become a part of a particular class of network, from A to E.
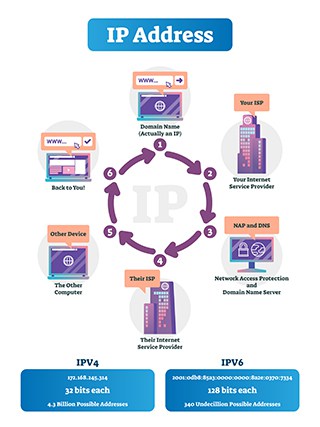
Another way to look at IP addresses is the sum of two parts: One part helps to identify the node/host, while the other assists to identify the network.
Any IP address’s class can be determined from the network it belongs to. Any two nodes that exist on the same network must have a unique host number but the same network prefix number.
What Are the Purposes of an IP?

The main purpose of an IP address is to manage any communication line between two devices that want to receive and send data to each other over a network.
IP addresses are also needed to identify every device on a given network (which can be the entire internet) with a unique number. Without IP addresses, there would be no way for two devices to identify each other.
One other purpose for which IP addresses are needed is when a user’s device wants to communicate with a streaming service and/or website. An IP address is the only way websites can identify the device trying to connect to them.
Which Devices Have an IP Address?

Examples of devices that have an IP address are given below.
- Smartphones
- Tablets
- Smart watches
- Desktop computers
- Printers
- Scanners
- Laptops
- Personal digital assistants (PDAs)
- Smart TVs
- All Internet of Things devices
What Information Does an IP Address Reveal?

The information an IP address reveals is given below.
- Zip code
- City
- Area code of the internet service provider (ISP)
- ISP’s name
- The IP address of the router
Types of IP Addresses
The types of IP addresses are given below.
- Consumer IP addresses
- Private IP addresses
- Public IP addresses
1. Consumer IP Addresses

Consumer IP addresses can be the web browser IP address of a user that has just purchased a product from an online platform or the payment gateway IP address used to submit the transaction. Businesses and online platforms usually use consumer IP addresses to create profiles on their users and analyze the activities users engage in on their platform, service, app or website.
The benefit of consumer IP addresses is that businesses can know more about their customers and what their needs are. Another advantage is that businesses can serve their customers better while providing support for a product or a service.
The main disadvantage of consumer IP addresses is that they take away the customer’s privacy and anonymity. Some businesses also abuse consumer IP addresses to invade their privacy and monitor their activities only to sell their data to the highest bidder on the internet.
2. Private IP Addresses

Private IP addresses are the IPs of each device that is connected to a user’s home network. Anything that can connect to the home network must have a private IP address, including smartphones, tablets, computers, smart TVs, IoT devices, printers and scanners.
The main benefit of private IP addresses is that the user’s router can identify all the devices connected to the network uniquely. The devices on the same home network also need to identify each other to communicate, and without a private IP address, these devices would not achieve that.
Private IP addresses enhance security since the devices on the home network are not directly connected to a larger external network or the internet. This makes sure common internet threats remain ineffective.

Another advantage of using private IP addresses is that each device on the home network does not require the internet to communicate with the other device. Moreover, since the whole setup is local, any problems that arise can be fixed instead of waiting for the ISP to provide a solution.
The main disadvantage of private IP addresses is isolation. Devices on the home network may be able to talk to other devices on the same network, but they can’t communicate with other devices on the internet. That means no checking email, accessing maps or contacting different vendors or suppliers to get work done.
Note:
Private IP addresses must be maintained by the local network operator. Any problem that may arise has to be fixed by the network operator, as ISPs and millions of other users on the internet can’t help.It is also impossible for two devices to have the same private IP address.
3. Public IP Addresses

The public IP address is the IP address of the user’s entire home network.
The main usage of public IP addresses is when devices outside the user’s home network want to connect to the devices inside the user’s network. Online IP address lookup tools also show public IP addresses to users who want to see them.
Any activity that the user carries out in the online world is ultimately tied to the public IP address. Public IP addresses are also used to run web servers, databases, email servers, API endpoints and many other activities.

The main benefit of using public IP addresses is that devices from any part of the world can send data to the user’s device by using the home network’s public IP address. Public IP addresses also identify devices on the internet without which no other device would be able to contact the user’s device or devices. Public IP addresses make it easier to configure devices on a network and solve connectivity issues.
The main disadvantage of public IP dresses is that the public IP address by its nature is available to the public and is accessible. This allows hackers a chance to find devices and inject them with malware.
What Are the Classes of IP Addresses?
The different classes of IP addresses are given below.
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
What Are the Examples of IP Addresses?
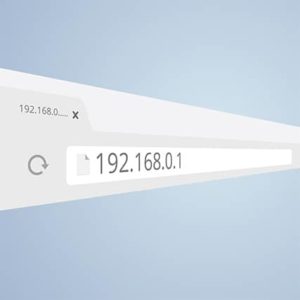
The examples of IP addresses are given below.
Most IPv4 addresses consist of two parts: The host ID and the network ID.
“192.168.1.10”
In the above example, 192.168.1 is the network portion and the .10 is the host portion.
A Class A IP address may look like 125.255.255.255 (Class A IP addresses can take values from 0.0.0.0 to 127.0.0.0). The 125. is the network ID and the 255.255.255 is the host ID. That is because for Class A IP addresses from the four sets of numbers, the first set is the network ID and the remaining three are the host ID.
A Class B IP address (which can only take values from 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255) can look like 156.212.213.214.
In the example above, 156.212. is the network ID and 213.214 is the host ID. For Class B IP addresses, the first two sets of numbers represent the network ID, while the last two sets of numbers represent the host ID.

For Class C IP addresses, the range is from 192.0.0.0 to 223.0.0.255. An example would be 192.0.0.12.
Here, 192.0.0 is the network ID and the .12 is the host ID. For Class C IP addresses, the first three sets of numbers represent the network ID and the last set of numbers represents the host ID.
Class D IP addresses can take any value from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. An example is 226.154.90.27.
Finally, Class E IP addresses can range from 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255. An example is 241.211.54.13.
What Are the Types of Public IP Addresses?
The types of public IP addresses are given below.
- Dynamic IP addresses
- Static IP addresses
1. Dynamic IP Addresses

Dynamic IP addresses are temporary in nature. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) servers assign dynamic IP addresses to all devices connected to a network. The DHCP server also configures the dynamic IP address automatically for existing devices on the network and any new device connected to the network.
Most usage cases of dynamic IP addresses involve internet service providers and home networks. In any situation where there is a chance of static IP addresses running out (as in the case of IPv4), dynamic IP addresses come into play.
The main benefit of using dynamic IP addresses is lower maintenance costs. Dynamic IP addresses are also more secure as hackers can’t pin down a particular device with a specific IP address. Dynamic IP addresses allow VPNs to stop tracking easily. And, due to DHCP servers, implementing dynamic IP addresses is easier. Dynamic IP addresses are also reusable and hence offer more flexibility.
The main disadvantage of using dynamic IP addresses is difficulty in enabling remote access options since the home network is always using a different IP address. Dynamic IP addresses are more prone to technical problems and may not work with geo-location services. Moreover, dynamic IP addresses require more maintenance, which means more disconnections than normal. Users looking to host servers or websites should also avoid using dynamic IP addresses as DNS systems have trouble working with dynamic IP addresses.
2. Static IP Addresses

Static IP addresses are permanent IP addresses that ISPs attach to specific broadband connections.
Businesses usually prefer static IP addresses over dynamic IP addresses. Home users may also need to use static IP addresses when they want to set up a home file server or install a new router. Users also must use static IP addresses for remote access sessions. Some devices require static IP addresses during port forwarding.
The main advantage of using static IP addresses is easier time running servers, as it’s simpler for other devices to find the server with a static IP address. Similarly, static IP addresses make remote access activities easier since the device to be accessed is not changing its IP address periodically.

Network administrators also find it easier to maintain networks with static IP addresses. Assigning a static IP address to a device is also easier. Admins can use static IP addresses to set access rights for different users and monitor internet traffic.
Due to static IP addresses being static, these IPs offer more stability for the user’s internet connection.
The main disadvantage of using static IP vs dynamic IP is that no other device can use a static IP address that has been assigned to another device, even if that device is not being used. Static IP addresses are unique to devices and hence not re-usable, which severely limits the total number of IP addresses. Static IPs can also cause privacy and anonymity problems as trackers find it easier to record information on devices with static IP addresses that don’t change over time.
What Are the Website IP Addresses?
Website IP addresses are assigned to servers and websites that offer digital services. Users can type a website address in the URL bar of the web browser and the web browser takes the URL address as a request from the user and sends the request to DNS. The DNS then translates the website address to a website IP address.
1. Dedicated IP Addresses

Dedicated IP addresses refer to IP addresses that are exclusive to a given user. No other website can share the dedicated IP address assigned to another user or a website.
The main advantage of dedicated IP addresses is that it’s easier to set up and run an FTP server for resource sharing. Remote access is also easier on a dedicated IP address. Dedicated IP addresses are also better for activities such as gaming since there is less downtime and interruptions to gameplay.
Cost is the main disadvantage of using dedicated IP addresses. Dedicated IP addresses are expensive when compared to shared IP addresses. Moreover, finding a good hosting service for a dedicated IP address is also difficult, since most hosting providers don’t offer such facilities. Dedicated IP addresses are also not ideal for low-volume internet traffic. And since the IP address is linked to a single user, a dedicated IP address can hurt privacy.
2. Shared IP addresses

Shared IP addresses refer to IP addresses that are not exclusive to any one particular user, website or server. With shared IP addresses, a website may have a specific IP address that also belongs to many other websites, services or servers.
In the context of VPN services, shared IP addresses mean multiple users will have the same IP address.
The main advantage of using shared IP addresses is increased privacy since activities carried out via the IP address are attributable to multiple users. VPN services that offer shared IP addresses are cheaper than those offering dedicated IP addresses. Shared IP addresses, in the context of a VPN service, are better for circumventing geo-restrictions and engaging in P2P file transfers such as torrenting.

The main disadvantage of using a shared IP address is that any abusive activity, like spamming and cyberattacks, carried out by another user on the same IP address can lead the user into trouble. More specifically, users with shared IP addresses will have to complete more captcha tests than users who have a dedicated IP address. Services and apps find it easier to block shared IP addresses.
Note:
Compared to a shared IP address, a dedicated IP address offers more security, less downtime and faster speeds since a single user or website has access to the dedicated IP address and the associated resources.On the other hand, in the debate over dedicated IP vs shared IP, shared IP addresses offer more privacy, economy and availability.
What Are the Subnetworks of an IP Address?
The subnetworks of an IP address are networks that exist inside of another network and are hence called subnetworks. Subnet masks are only used for internal purposes within a given network.
What Is an IPv4 Address?

An IPv4 IP address is a type of IP address that consists of 32 binary bits. Most of the time, a given IPv4 address has two parts: The host ID part and the network ID part. A subnet mask helps to divide IPv4 addresses into these parts.
The IPv4 address is further broken down into four octets, each representing eight bits. To complete the IPv4 address, each of the four-octet sets is converted into decimal form and then a period is placed between them for separation.
Examples include, 192.168.108.111, 254.14.23.12 and 127.0.0.1.
Any octet from the four sets can contain values from 0 to 255.
What Is an IPv6 Address?
IPv6 addresses are the type of addresses that use 128 binary bits. The address remains a single string of numbers.
In the case of IPv6 addresses, there are eight sets of numbers and alphabets separated by “:”.
Examples include 4dde:12800:4345:2:100:f8dd:ef42:76fc and 21CA:A3:0:3D3B:2BB:GG:JF91:7D6A

What Is a Local IP Address?

The local IP address is the IP address that a device or any other internet-enabled machine gets assigned when it becomes part of a network. Local IP addresses are hidden from the internet, and one can only access the local IP address via the local network.
Examples include devices that are part of the local network at a library, office or university. Any device on the office’s network can communicate with other devices on the same local network. But devices from outside the network, such as those connected to the internet or in a local network at another university, cannot.
What Is an External IP Address?
The external IP address refers to the IP address that an internet service provider assigns to its customers. All other devices and entities on the internet see this IP address.
This is important:
A device on a home network may have an IP address such as 192.168.1.20 and another device on the same home network may have an IP address 192.168.1.12. But both would have the same external IP address, which may look something like 110.155.231.154.How to Look Up IP Addresses?

The method to lookup IP addresses is given below.
For Windows, users have to run Command Prompt as administrator and then use the command “arp -a” (without the quotes) to view all IP addresses.
Third-party applications, like Wireless Network Watcher from Nirsoft, can also scan the network and list the IP addresses of the devices connected to a given network.
For Linux, users should open up the terminal and use the command “arp -v” to view IP addresses. They can do the same using the third-party application Angry IP Scanner.
Use the command “sudo apt install openjdk-14-jre” for Java and then get the Angry IP Scanner package from the official website. Once downloaded, double-click it to install Angry IP Scanner. Launch the Angry IP Scanner and press scan to view the IP addresses of the devices on the current network.

On macOS, open the terminal app and type “arp -a” to view IP addresses. The Mac App Store also offers an app called LAN Scan that can look up IP addresses.
For Android and iOS devices, the best app to lookup IP addresses is Fing. Get Fing from the Apple App Store or Google Play Store, install and launch the app, then press the button “scan for devices” to know the IP addresses of all devices on the network.
Ïf you want to find an automatic tool on how to find your computer’s IP address, then use our free tool. Some websites that can look up IP addresses are given below.
- Whatismyipaddress.com
- Ipleak.net
How the Others Can Find Your IP Address?

Others can find the IP address of any device connected to the internet using a variety of methods.
The most convenient way is to physically get access to the device a user has. All that others have to do to find the IP address of the user (once they have the device in hand) is go to a website like whatismyipaddress.com and check.
If the “others” refer to law enforcement agencies, these officials can know the IP addresses of anyone under investigation with a subpoena.
Links that take the user away from the messaging app they’re using to communicate with another person can also be used to find out the user’s IP address.
Social media platforms can also find users’ IP addresses if the site administrators deem it necessary. Once a user clicks on a link, the platforms can capture the user’s IP address. Similarly, blog administrators can know the user’s IP address if the user has left a comment on the blog.

Another way to find any user’s IP address is to access an unsecured wireless network the user may be on. Malicious actors can even use the user’s wireless network as a guest to find out the user’s IP address.
Sometimes HTML bugs are also used to know the IP address of a given user. This method doesn’t always require malicious code or a virus. A malicious actor can embed a small piece of code in something as benign as an image in an email. If the user views the image, the malicious actor can know the user’s IP address.
Is It Dangerous for People to Know Your IP Address?

Yes, it is dangerous for people to know the IP address of a given user’s device.
If some malicious actor knows the IP address of the user, the malicious actor can launch DDoS attacks on the user’s router. Hackers can also know the user’s general location (city, state and sometimes even the specific area) if the user’s IP address is exposed.
Cybercriminals can also report the user’s IP addresses to various databases to get the user on a blacklist of IP addresses. Less dangerous cases may involve someone reporting the IP address of the user to law enforcement agencies for potentially illegal activities such as torrenting or spam.
Note:
Generally, hackers can launch all sorts of attacks on a user with a leaked IP address. Whether or not those attacks are successful depends on how the user has set up security on internet-enabled devices.What Are the IP Addresses of Big Websites?
The IP addresses of big websites are given below.
- Google.com – 172.217.11.174
- Mediafire.com – 205.196.120.13
- Bbc.co.uk – 212.58.241.131/
- Wikipedia.org – 208.80.152.2
What Can be Done Through Someone Else’s IP Address?
Examples of things that can be done through someone else’s IP address are given below.
- An admin or service can ban someone from an online game.
- Different organizations can sue a person for downloading illegal content from torrenting sites (only in some countries).
- Cybercriminals and advertising companies can show someone unwanted ads.
- Hackers can know the specific location of the user via phishing attacks after finding the IP address from the ISP of the user.
- Malicious actors can also sell IP addresses to database builders on the dark web.
- Streaming services can ban users via their IP addresses if users violate the terms of agreement or try to circumvent geo-restrictions.
1. Downloading Illegal Content Using Their IP Address

Hackers or other types of cybercriminals can gain access to a home network and then use the IP address of the home router to download illegal content—all the while the user is unaware of the process.
And if the laws on torrenting in the user’s country are strict, the user can get into legal trouble. Copyright-holding groups and law enforcement agencies monitor torrenting traffic and can isolate a given user’s IP address, contact the ISP of the user and demand the user’s exact location. Once law enforcement agencies do that, the user can either pay a fine or face a DMCA notice or go to jail.
Pro Tip:
Users should use a VPN service to make sure their real IP address is hidden and hence no one can exploit their IP address to download illegal content.2.Tracking Down the Location

A skillful enough hacker (and as mentioned before, law enforcement agencies) can use the IP address of the user to find out the ISP serving the user. Then hackers can dupe the ISP into giving up the user’s personal information. Once that happens, hackers can easily know the real location of the user.
The chances of that happening are very low unless one works on sensitive national security-level projects on a regular basis. Nevertheless, users should install a VPN to hide their real IP address and stay safe.
This is important:
As a precaution, users should avoid giving their public IP addresses on any online forum or messaging apps.3. Online Stalking

If someone has a user’s IP address, that is usually not enough to know the exact location of the user. But such information is enough to track down this individual’s social media profiles and stalk them. Once the stalking starts, cybercriminals can know more personal information by keeping tabs on the user’s activities via social media profiles.
Once hackers have enough personal information from such activities, hackers can move on to the next phase and blackmail the user.
Note:
An obvious precaution is to not give out one’s IP address on a public forum and always use a VPN service to change one’s IP address. This way, hackers can’t get to the real IP address of the user.4. Hacking Into Their Devices

Cybercriminals with enough skills, resources and infrastructure can use the user’s IP address to look for any open ports on the user’s device. In a case where hackers discover an open port, hackers can control it. From there, hackers can also gain control of the user’s device and then use the device for executing commands remotely.
Phishing attacks are another method to hack into devices after identifying the target IP address. Upon success, hackers then trick users into downloading malicious apps on their devices. Once that happens, it is possible for hackers to have remote access to the device.
To guard against that, users should make sure their operating system is always up to date. Moreover, install a good antimalware or antivirus product. It is always a good idea to keep the firewall that comes with Windows turned on and regularly use applications like Malwarebytes to keep everything clean.
5. Directly Attacking Their Network

Cybercriminals can inflict a lot of damage if they somehow get a user’s IP address and are determined enough to cause harm by directly attacking the user’s network. Among the types of attacks where hackers directly attack a network, DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) is currently the most popular.
In a DDoS attack, hackers essentially overload the user’s network with excess traffic. Once that happens, the network stops responding. If the user is hosting a website on the network, the website would go down. In other situations, if the user is playing an online game, the connection to the game would be lost.
And once again, the best way to guard against such problems is to use a VPN and hide the IP address.
How to Change an IP Address?
There are several ways to change an IP address, given below.
The easiest and the least time-consuming way to change an IP address is to use a VPN service. To use a VPN to change an IP address, the user first has to pick a good VPN service and then sign up for a subscription package. After that, the user has to download the app of the selected VPN service from the provider’s website and then install the app. After launching the app, the user has to input login credentials and connect to a server to change the IP address.
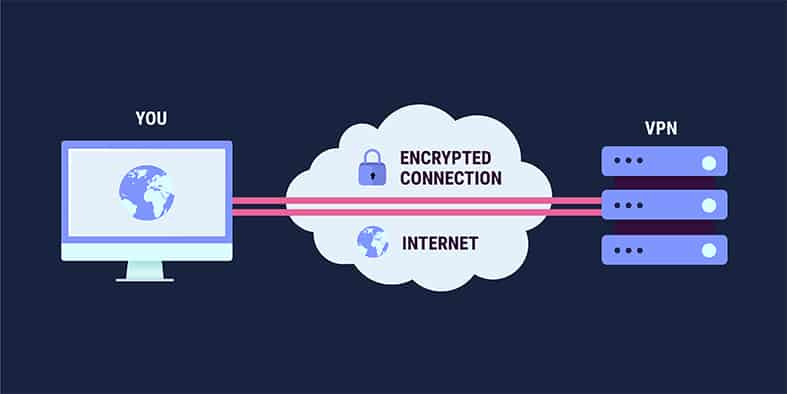
The above method works for all platforms such as Windows, macOS, Android and Linux.
Another way to change an IP address is to simply power off and unplug the WiFi router for around 10 minutes. During this time, the router should forget the user’s device. Once turned back on, the router will automatically assign the user’s device a new IP address.
A third way to change an IP address is via the Settings menu of the device in question.
On Android, the user first has to go to “Settings” and then to “Connections,” then to “WiFi” and then select the current active WiFi network. Tap the icon in the shape of a great in front of the WiFi network’s name and then tap the “Forget” option at the bottom on the new screen. The phone will disconnect from the network and forget the user’s device. Upon reconnection, the network will change the IP address of the user’s device.

For Windows 10 users, press the button with the windows icon on it and the “R” key together and type “cmd” in the Run window that opens up. From the new black window, type “ipconfig /release” and hit enter. Then, type “ipconfig /renew” and press the enter button one more time.
On the iOS platform, tap on “Settings” and then go to “Network.” From there, tap on the active wireless connection and then go to the section labeled IPv4. Click on “Configure IP” and then tap on “Automatic.”
For macOS, click on the button in the top left portion with an Apple trademark sign. Then, go to “System Preferences” and then click on “Network.” After that, go to “Advanced,” then click on TCP/IP. Finally, click the “Renew DHCP Lease” option.
Is It Possible to Generate a Random IP Address?
Yes, it is possible to generate a random IP address.
The first way is to simply wait for the ISP to assign a randomly generated new IP address. Every time that happens, the user will experience temporary connection loss.
Another method is to use a proxy service that offers a rotating IP address feature. Some websites that can generate random IP addresses are www.ipvoid.com, www.browserling.com/tools/random-ip and onlinerandomtools.com/generate-random-ip.
How to Protect and Hide Your IP Address?

It is possible to protect and hide IP addresses, and the best way is to use a VPN.
The steps to protect and hide IP addresses involve first signing up for a premium VPN service. After that, download the VPN app from the official website of the VPN service. Launch the VPN app and then sign in. Finally, connect to a server from the list and, thus, hide the IP address.
Since any VPN service usually has access to all user data, users must make sure the VPN ranks high on trustworthiness. Ideally, the VPN service should keep zero logs or the minimum amount of logs for operation. The VPN should also not sell user data to advertisers and marketing companies.
This is important:
Users should take the time to read the privacy policy of not just the VPNs but also any other software programs installed on any device. The user should then update all the software on the given device and make sure the router used for internet access doesn’t have the default password.For users with extra privacy concerns, using Tor is a must. To use Tor, users can either sign up for a VPN that offers features such as VPN over Tor. Or use the Tor browser, a free program developed by the Tor Project.
Users should also always use mainstream web browsers like Firefox and Chrome in incognito mode so that the browser does not cache data and store cookies and history on the user’s device.
To further hide IP addresses for enhanced privacy and anonymity, users should try and use end-to-end encrypted email services such as ProtonMail or Tutanota. Instead of communicating online via WhatsApp or Skype, users should use Wire or Signal for better privacy and data security.
Pro Tip:
Users should also encrypt their devices (both desktop and mobile) for more security and anonymity.Choosing unique and strong passwords is also a must for greater data security and privacy. Password managers can help with this. Currently, LastPass and BitWarden are among the best password managers.
When using two-factor authentication (2FA), always go with authenticator apps rather than SMS authentication, as hackers find it easier to compromise SMS-based 2FA.
What Is the Relation Between a VPN and an IP Address?
VPN (virtual private network) services hide IP addresses and user data via an encrypted tunnel. Any data that the user’s device generates goes through the encrypted tunnel for privacy and anonymity. Modern VPN services can also change the user’s IP address to any location in the world.
New IP addresses essentially hide the user’s online identity. With each VPN server assigning the user a different IP address, the user has a lot of opportunities to improve privacy and anonymity online.
When Should You Use a VPN for Your IP Address?
The situations where an online user should use a VPN for hiding IP addresses are given below.
- If a website has blocked a user’s current IP address, VPN services can change the IP address to unblock the website/service/app.
- VPNs should be used to carry out any activity that requires enhanced security such as banking, shopping, accessing medical records and communicating sensitive information.
- VPNs should be used when users want to work remotely and need to access classified and sensitive documents from office servers.
- Businesses can require workers to use a VPN to safeguard company information.
- VPNs can secure public networks in places such as cafes, restaurants, airports, local libraries and gyms.
- While traveling, VPNs can protect user data from hackers on a mobile internet connection.
- Whenever there is a need to circumvent geo-restrictions, VPNs have a role to play.
- Users should use VPNs when they want to access better versions of streaming services for more content, such as U.S. Netflix or the U.S. version of YouTube.
For information on how to use a VPN service, we have you covered in an easy to use guide.
What Are the Other Ways to Protect Your IP’s Privacy?
Other ways to protect your IP’s privacy are given below.

- Use antivirus products to protect IP privacy.
- Password lock smartphone devices to enhance privacy.
- Keep all software updated for enhanced data protection.
- Only download apps from trusted sources to keep away from malicious apps that violate privacy.
- To guard against privacy invasion, not click on links that come from questionable or unknown sources.
- Always verify if the website opened is a legitimate one instead of a malicious copy of a legitimate website.
- Check URLs by hovering over them before clicking them for a safe online experience.
- Use anonymous search engines instead of Google, which relies on IP addresses to connect searches made to user profiles.
- Do not share personal information on online forums.
How to Ping an IP Address for Testing Connectivity?

To ping an IP address for testing connectivity, the user has to use the “ping” command. This command works on all operating systems, such as Linux, Windows or macOS.
Users should press the “R” key while holding down the “Windows” key to open the Run window. Then, type “cmd” (without the quotes) into the text box in front of “Open.” From the new black-colored window, type “ping” and then type the URL of the website to check for connectivity. To ping Google, type “ping www.google.com.”
If there are no connectivity issues, the screen should show the IP address of the URL and the packet size sent to the URL. After that, all the subsequent lines will show information such as time for a response, individual packet replies, and the time after which a given packet is tossed out.
How to Block an IP Address?

To block an IP address, the user can use the cPanel to go to “Security” and then to “IP Deny Manager.” From there, the user should input the IP address to be blocked—and that’s it. The hPanel from Hostinger can also block IP addresses via its Deny Box option.
Users can also block IP addresses via the administrative page of the router. To access the router, users can input 192.168.1.2 (or 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1 or whatever the IP address of the router is (it’s usually written on the bottom of the router) into the URL bar of any mainstream web browser.
After logging in, the user should look for configuration pages labeled Firewall or Block Websites, which are usually found either under Parental Filtering or Content Filtering. From there, the user should go to Security and input the IP address on the configuration page. Usually, the input box for an IP address has the text “keyword” or “domain name” written on it. But the box works for IP addresses as well.
Once done, the user should hit the “Done” button and then the “Save” button.

Another way to block an IP address is to use the Windows Firewall via the Control Panel. Users should launch the Windows Firewall app and then go to “Inbound Rules.” From there, go to the new Rule and then click on “Custom.” Then, click “Next” and then “All Programs.” Click next again and then click “These IP Addresses.” Then click “Add” and then input the IP address to be blocked. Then click “OK” and then “Next.” From there, select the menu for “Block the Connection” and name the new rule. Finally, click the finish button.
Some of the methods mentioned above will also work for macOS users.
One method specific to macOS users is via System Preferences. After clicking the Apple icon in the top-left corner of the screen, the user should click on “System Preferences.” Then, go to the “Network” option and then click on “Advanced.” From there, go to the tab labeled TCP/IP and then input the IP address to be blocked.
What Are the Problems and Solutions of IP Addresses?
The problems and solutions of IP addresses are given below.

- IP address conflict is a problem that occurs frequently in some settings. IP conflict usually arises because two devices on the same network get assigned the same IP address. Restarting the router usually fixes the problem as the router will assign devices on the network new IP addresses.
- An invalid IP address is another common IP troubleshooting avenue for network administrators. This problem doesn’t come with a statement but usually cuts off the web browser’s ability to load websites. The invalid IP address problem also disables file transfer between two devices on the same network. To fix the problem, the user should first change the network and then restart that device. If the problem persists, the user should limit the number of DHCP servers. Similarly, clearing TCP/IP temporary files and cache can also sometimes solve the invalid IP address problem.
- The “IP Address Could Not Be Found” or “DNS Name Doesn’t Exist” warning messages may arise because the DNS has not been configured properly. Users facing this problem should configure their network devices to use DNS servers of their own and hence not pay attention to the DHCP assigned server. Under the TCP/IP Settings, the network adapter usually shows the DNS server (which may be incorrect). In such cases, the user should check the option “Obtain DNS server address automatically.”
- IP address exhaustion is another problem. If a device has assigned itself an IP address beginning with 169.x.y.z, this error can arise. Users with no local routers usually get assigned IP addresses by their ISP. Once these run out, the user has to get a new router or any device that can act as a WiFi access point. That should get rid of the problem as the router would offer its own pool of internal IP addresses.
- IP address duplication causes network access to cease. The solution to this problem is to disable any new device’s DHCP server. Yes, new devices connected to a given network can mess with the router’s default DHCP configuration.

