Fake IP addresses, arguably bear some resemblance to the act of hiding in plain sight. IP spoofing, the act of hiding an IP address, is camouflaging a computer’s IP address while making this address appear real. A person seizes control of a network with the help of a fake IP (Internet Protocol) address during the masking process. Faking an IP address involves hiding IP headers through a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and manipulating the crucial information in the header.
Hiding an IP address is necessary for various reasons, one of the most important being protecting an individual’s privacy while using the internet. Internet service providers, search engines and advertising networks can easily track the address and monitor a person’s online activity. IP spoofing also helps individuals protect devices from hackers, access geo-restricted content and safely browse using public Wi-Fi. Unfortunately, Internet Protocol spoofing is illegal in a lot of countries worldwide. There is a common misconception that the act is only used to support malicious activity, like cyberattacks on computers. Some IP spoofing practices are legal, though. For instance, network administrators can use IP addresses to troubleshoot a system error without remotely logging in.

Table of Contents
What is a Fake IP Address?

An IP address is an exceptional address that recognizes a device, a computer, for example, on a local network or the internet. The address is a major identifier that enables the communication between two or more devices on the internet. This ability comes from the local information, making devices send or receive information on a network. Anyone who intends to use the internet or perform any online activity cannot do so without an IP address. These addresses are very important to help the internet distinguish different websites, computers and routers. IP addresses form an integral part of the internet’s operations.
IP is the short form of Internet Protocol, a set of regulations that administer any data format sent through a local network or the internet. The IP generates an address using a sequence of numbers disconnected by periods. The full IP address numbers range from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255. This doesn’t mean that IP addresses are randomly picked and assigned to a device. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is a USA non-profit organization that mathematically produces and allocates IP definition.A fake IP address is devoid of credibility in Internet Protocols frameworks. These addresses help individuals access the internet and browse without the address revealing mobile devices and computers’ real identity or location. Europe and the USA have strict laws that limit the use of fake IP addresses. This is because governments monitor online activities to identify threats against computer systems. Other foreign countries with more flexible laws are the bedrock of servers holding false IPs.

Using unsecured public Wi-Fi can expose a user’s gadget to cyberattacks. If the user doesn’t hide the computer’s IP address, hackers can gain access and maliciously compromise the device’s functions. Many people use fake IP addresses to encrypt internet connections when using public Wi-Fi, unblock websites, hide locations, avoid being tracked or access blocked content. Another fake IP address use is to avoid being tracked. Browsing on the internet without a device being tracked can be impossible. Individuals keen on protecting their privacy by masking their internet activity use fake IP addresses to browse the web privately.
One can also access blocked content through a fake IP address. Otherwise, individuals wouldn’t be able to access geographically restricted content. The restrictions may be due to copyright regulations. Hiding a device’s IP address means that the device’s location is unknown. Therefore, an individual can easily download or stream content from sites.
Dodging government restrictions is another fake IP use. Some governments closely monitor internet activities and censor content that seems to contradict their laws. This includes citizens supporting online anti-government movements. Accessing such content could spell trouble for individuals in these jurisdictions, causing them to face criminal charges. Individuals who don’t appreciate the censorship could use fake IP addresses to browse online.
Using a fake IP address is important because it helps protect users’ online privacy. Hiding an internet user’s IP address ensures a discreet browsing session without being tracked by ISPs, governments, hackers and ad networks.
Note:
Hiding an IP address has many benefits, including users experiencing fewer ads. Ad networks cannot track down an internet user who has accessed certain websites using false IP addresses. Also, they enable users to enjoy a safe browsing experience even on public Wi-Fi without leaving traces of their device details behind.Another benefit is that individuals using a false IP address are less likely to be jailed when visiting certain sites under government censorship. Gaming fanatics also enjoy the anonymity hidden IP addresses provide when playing online video games.
How to get a Fake IP Address
1. Use a VPN

A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a simple way of connecting devices like computers to a different person’s network. Any online activity that an individual engages in appears to be coming from the other network and not the actual one. No one can trace the real device’s identity using a VPN unless the identity leaks via DNS (Domain Name System).
The most effective VPN that won’t succumb easily to DNS leaks is a paid version. Free VPNs are quite vulnerable to many risks and disadvantages, like selling users’ data and giving up real IP addresses. Therefore, users shouldn’t put all their trust in them. Logless VPNs are the best because they don’t store users’ activity logs, making it impossible to reveal IP addresses. Also, most of them encrypt users’ internet activities on the network to prevent tracking.
When one has installed a VPN on a device, all the network traffic from the device is diverted via a protected connection to the Virtual Private Network. No matter the user’s location, one can easily and securely access local network resources because the VPN acts like being on the same network. A user can also use the internet under the guise of the VPN’s location even when not physically there. This is especially helpful for individuals who want to access geographically restricted content or use free Wi-Fi.
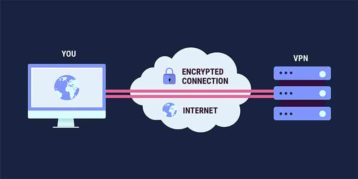
If an individual browses the internet while connected to a VPN, the device uses an encrypted VPN connection to signal the website. The VPN acts as the middleman between the user and the web by forwarding requests to websites. When the websites respond, the VPNs use a protected connection to forward the response back to the user. For example, if one uses a France-based VPN to stream content on Hulu, the company will see that the connection is within France.
OpenVPN is one of the most popular VPN tools currently available. An easy-to-setup open-source VPN server. One can effortlessly transfer configuration files from this tool and import them to various commercial and open-source clientele. Tomato, OpenWRT and DD-WRT are some of the router microcode packages with the OpenVPN system. However, popular commercial VPN providers are not adaptable to this system. Despite this limitation, OpenVPN is a free and open-source alternative to closed and pricey options when setting up VPNs.
Cisco VPN is also a Virtual Private Network tool compatible with Mac, Windows and Linux and is mostly used in educational and corporate settings. The price of running this VPN varies because one has to get a quote from the company. The end-user can download the free version (Cisco VPN client) and use the VPN on Windows and Mac devices.
Shrew soft VPN is a free VPN tool users can utilize in Linux or Windows systems. The VPN works with various VPN server protocols like strongSWAN, freeSWAN and OpenSWAN.

Also, there is LogMeIn Hamachi, a free and easy-to-use VPN that one can instantly deploy on all devices and machines (Mac, Linux, Windows). One can install the Hamachi client, connect to the network and add to the Hamachi VPN.
One of the greatest benefits of using VPNs is concealing a user’s real location, maintaining their online privacy when browsing the internet. VPNs also help users stream favorite shows or movies from media giants like Hulu, Netflix or Showmax. They enable individuals to access geographically restricted content on websites while preventing snooping on devices. Finally, VPNs benefit users by protecting them from being logged while downloading or uploading files via the BitTorrent network.
Some VPNs’ logging policies are questionable, especially where providers store devices’ data logs. This leaves a user’s information susceptible to being tracked, contradicting the intention of having a VPN.
Another risk of using VPNs is that the security may be subjected to the country where the system’s servers are. If a VPN is located under a jurisdiction with strict data retention regulations, the VPN has to store a user’s information. Also, if certain apps are restricted in the country where a VPN is located, the VPN prevents a user from another country from accessing those apps even when their own countries permit them.

Speed is also among the potential VPN risks. A user may experience a slower connection while using a VPN-enabled smartphone, limiting their browsing experience. Some individuals may be disappointed to learn that the free VPNs they relish so much have to earn revenues by selling user data to third parties. Hence they are not so private, after all.
To set up, get the VPN service of choice. Ensure the service is compatible with the devices. Also, consider the service’s functionality. The process of setting up the VPN usually involves downloading the app, installing and signing into the app with the VPN account. Choose the server by selecting the country the device networks will connect to. And the VPN is now ready to use.
2. Use a Web Proxy

A web proxy works as a VPN to hide a gadget’s IP address. The individual connects to the proxy server, making the web traffic pass through the server. The gadget’s IP is concealed under the proxy server’s IP address. However, web proxies are not encrypted, making them susceptible to governments and internet service providers snooping.
Web proxies help protect computers from cyber threats like malware. Individuals can set proxies up as firewalls or website filters to provide computers with internet security. Web proxies also work well when combined with email security brands or secure web gateways to provide an extra security layer. Companies and individuals use web proxies for different reasons, including hiding the real IP address of gadgets. Enterprises use them to restrict the websites that employees can visit while working in the offices, protect company computers from cyber threats, compress incoming traffic or cache files to save bandwidth and prevent crashes on the company systems by balancing the internet traffic.

Some of the web proxy tools available in the market today include Fiddler. Fiddler is a proxy that individuals use to debug the web. The proxy logs all Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) between the internet and an individual’s computer. Using Fiddler enables individuals to interfere with outgoing or incoming data and to set breakpoints and examine all HTTPS traffic in the system. Fiddler has a robust scripting subsystem that is event-based, allowing individuals to extend it via any .NET language.
Another web proxy tool is Ratproxy. This web proxy is semi-automated and mainly passive when used as an audit tool in web application security. Ratproxy largely complements manual proxies and active web crawlers generally used in web security. The web proxy is also optimized for automatic interpretation and detecting potential hitches and security-related design systems. Ratproxy does this by observing the prevailing user-originated traffic in intricate web 2.0 contexts.

Paros proxy is a java-based web proxy tool that individuals use to examine vulnerabilities in web applications. The web proxy enables users to change items like form fields and cookies by viewing or editing HTTP or HTTPS messages on the fly. Paros proxy has a scanner for testing frequent web application attacks, for instance, cross-site scripting and SQL injection. The proxy also has a hash calculator, a web spider and a web traffic recorder.
Also, there is sslstrip, a web proxy designed to strip SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) by making unencrypted HTTP sessions closely resemble HTTPS sessions. sslstrip does this by using a known private key to convert the HTTP links to HTTPs. The proxy also gives users the padlock favicon insinuating the safety of a website. Many users don’t realize that their connection hasn’t been upgraded because they usually access many HTTPS websites via being redirected from an HTTP page.
Note:
Using web proxies has many advantages for users, including hiding IP addresses to preserve anonymity while browsing the web. One can safely browse without being exposed to cyberattack risks like snooping. A web browser also protects devices from falling prey to hacker websites that users may be unaware of. The user’s device doesn’t make direct system requests to such sites; web proxies do. Therefore, the proxy pushes away the threats on behalf of users’ devices.Another benefit of web proxies is that users are enabled to access geo-restricted content due to copyright laws in various countries. Using the proxies essentially means one is using a fake IP address, enabling the access to content only available in certain regions.
Also, web proxies enable companies to exercise control over their systems. Companies do this by enabling employees to access certain websites only while working, improving their overall productivity. A proxy can also unlock certain websites out of reach to the general population.
Another web proxy benefit is the enhanced web browsing experience. Web proxies use cached data to store all the essential information when a user visits a website. The next time the user visits the same website, the page results are displayed much faster. This only happens when the web proxy has the required cached data from the website. If not, the proxy requests the information from the outlying server.

Some vulnerabilities associated with web proxy servers include the risk of falling prey to scams and virus attacks. Some proxy servers have many ads and banners that may threaten device security. Also, some proxy providers have malicious intent when prompting users to download certain software. Users who download the software may experience technical issues in used devices, including slowed-down browsing speeds.
Another potential web proxy risk is a broken internet caused by the servers’ heavy traffic load. Both free and paid proxy servers experience this problem that causes an inadvertently slow internet speed. This mainly occurs when the servers use a low bandwidth to host data from scores of other devices.
Security hacks are also part of web proxies’ potential risks. All the user details pass to and from websites via proxy servers. The data is at the mercy of the servers, leaving the data vulnerable to being compromised, especially if the server is malicious. Proxy servers also don’t encrypt the data that goes through them, facilitating cybercriminals to ambush and steal vital user information. Other servers may sell user information to third parties and breach privacy needs.
3. Use Public Wi-Fi

Public Wi-Fi allows individuals to access free internet. Wi-Fi is easily accessible to individuals in public spaces like malls, cafes, airports, hotels, restaurants and shops. Individuals use public Wi-Fi to connect directly to a certain network without routing the internet traffic via another person’s network. This enables them to hide the home IP addresses, impeding malicious parties to trace them. The Wi-Fi is used by dozens of people at a time and obscures individual users’ devices from being identified.
Some of the best tools that public Wi-Fi administrators can use to analyze, monitor and secure the networks include AirMagnet WiFi Analyzer Pro. This is an extensive tool developed by NetAlly. The software gives users a synopsis of how the network performs, the coverage and connectivity. AirMagnet WiFi Analyzer Pro also summarizes the Wi-Fi security concerns, including detecting Wi-Fi interference.
Acrylic Wi-Fi is a free Windows scanner that displays Wi-Fi information on the dashboard. The platform also has a paid version for professional settings. Acrylic Wi-Fi scans the user’s surroundings to identify nearby APs. The software obtains data, for instance, signal strength degrees, WLAN security encryption, channels and SSID. Individuals can use the information on display to troubleshoot and optimize Wi-Fi networks.

Another free Wi-Fi analysis tool is NetSpot. The tool conducts Wi-Fi analysis and surveys for macOS and Windows. NetSpot allows users to perform site surveys and scan a Wi-Fi network’s coverage scope. The software then displays the data in one dashboard to allow individuals to visualize the details. Users can also use NetSpot to identify the Wi-Fi dead zones or signal leakages through Wi-Fi heatmaps.
The InSSIder is a small-network Wi-Fi scanner designed by MetaGeek. The software performs various Wi-Fi scanning functions to help optimize the networks for better performance. For instance, InSSIder helps fix bandwidth challenges and identify trouble areas. The tool also helps recognize WiFi networks’ interference. Moreover, InSSIder can analyze a user’s WiFi and give alerts if there are better channels, detecting villain APs in the process.
Note:
Using public Wi-Fi to browse the internet means individuals don’t use home Wi-Fi, protecting them from exposing their IP addresses. Therefore, users are at less risk of being tracked to their real locations by cybercriminals. Also, multiple people use public Wi-Fi simultaneously, impeding the tracking of particular individuals’ internet activity.
Using public Wi-Fi is risky because most hotspots are not encrypted. Therefore, other users utilizing the same public Wi-Fi can see someone else’s internet activities if there’s the intention of spying. Cybercriminals can snoop on individuals’ online shopping activity, private login details and financial information over public Wi-Fi. The hotspots also carry a significant risk of spreading malware infections to the connected devices.
Identity theft is also a major concern when using free Wi-Fi. Hackers can use individuals’ personal information obtained from the network to commit crimes. The crimes may place an innocent individual at the crime scene because all the evidence points to this person and not the real criminals. While hiding one’s home IP address may sound like a fantastic idea, keep in mind all the above public Wi-Fi risks that would save anyone a lot of trouble.
4. Use Tor Browser

Tor browser is a free platform that individuals use to hide IP addresses when using the internet. The browser hides the IP address by connecting users to the Tor network at the beginning. Users can convey data through an indiscriminate relay server with the connection. The servers are hosted globally by various volunteers. The Onion router, another name for Tor Browser, is banned in some countries like Venezuela and China.
Individuals get started on the browser by visiting the Tor official website. Then, download and install the software from the website and set up. Once the setup is done, click connect to link to the Tor network. The process typically takes a few minutes to complete. Users are now free to use Tor and anonymously browse the internet. First-time users should utilize the security tips on the Tor website’s homepage to maximize the platform’s efficiency.
The Tor project is a not-for-profit institution that runs investigation and development activities into online invisibility and privacy. Individuals can test a Tor network without invading users’ privacy or running into deployment issues using various tools like Shadow. Shadow is a network emulator hybrid. This tool develops practical network topologies by utilizing excerpts of Tor directory data. Chutney is another Tor test network configuration tool. This tool launches and establishes connectivity between Tor processes. Chutney can also perform tests on CPU-confined bandwidth.

Enabling individuals to gain free access to websites that the network has blocked and hiding individuals’ online activity by resetting cookies and browsing history when the person has finished browsing the web are some benefits of Tor browser. The Onion Router also provides users with multi-layer encryption, meaning the user’s traffic is encrypted and redirected several times. This ensures that the user’s identity remains absolutely anonymous. Other benefits are that the software prevents other network users from tracking the websites that a Tor user visits and strives to maintain the anonymous identity of all users by making the identities seem identical. This prevents any malicious party from identifying any user based on device or browser characteristics.
Tor users regularly experience hacking incidents. The hacks occur because a user’s device doesn’t have thorough security measures. Tor is usually not the one to blame for such incidents. Every Tor user should be aware and alert that devices can be hacked anytime. The browser enables users to visit the dark web. The dark web is a hidden part of the internet that other browsers can’t access. However, visiting this web could spell disaster for Tor users. This is because the dark web is rife with criminals, malicious content and viruses that could severely harm a device.

Also, Tor users can still be tracked when using the internet, even under the browser’s protection. An individual controlling exit node (the last stop before an individual is connected to a web page) can see all the user traffic flowing within the system. That individual can see all the internet activity of a Tor browser user, making data not so private anymore.
Tor browser is simple to use. All users need to access the browser’s features to download and install on devices. Individuals can use Tor browser like any other browser available today. A recent Tor browser review lauded the open-source nature and how the software prioritizes user privacy. However, the review concluded that there are safer and easier-to-use Tor browser alternatives in the market today.
5. Use a Fake IP Address Generator

A fake IP generator is an online tool that individuals can use to generate “fake IP addresses.” Individuals like programmers and software developers use false IP addresses to perform cross-browser testing on online tools or applications. Note that fake IP addresses don’t exist in the real sense because one would need an actual IP address to browse the internet. However, random IP addresses do exist for software developers and programmers use.
The online tool develops fake IP addresses by randomly selecting every possible character that individuals can use on IPv6 or IPv4 addresses. The generator uses the JavaScript method {math.random()} to select the characters. IPv4 and IPv6 are the versions used for IP addresses.
Fake IP address generators help individuals generate random IP addresses. The benefits of using such addresses include individuals browsing anything on the internet without being tracked or watched. Individuals don’t have to worry about identities being involuntarily revealed. Also, fake IP generators preserve users’ anonymity and make internet browsing experiences safer.
What Extensions can be Used to get a Fake IP Address?

The extension software can be on Chrome or Firefox, helping individuals fake IP addresses. One example is ExpressVPN, an extension that helps users spoof HTML geolocations to preserve online anonymity. ExpressVPN also ensures that individuals use the secure and encrypted HTTPS website versions if available. Hotspot shield is another great option. Hotspot shield is one of the best fake IP extension software on the Chrome browser. The software enables individuals to access blocked content on websites and conceal IP addresses.
Touch VPN, a free-to-use extension, is touted as one of Chrome’s fastest and most effective fake IP extensions. This software changes users’ IP addresses without creating an account or logging in. When accessing the user-friendly interface, all users need is to download the extension and click “Connect” to hide their real IP addresses.
Individuals can also use SetupVPN, a Chrome and Firefox extension that effectively enables users to fake IP addresses. Individuals can easily maintain online anonymity with this extension that has military-level encryption. SetupVPN’s outstanding fake IP generation abilities also come from having a good bandwidth and approximately 100 servers globally. The VPN is free to download and use.

CyberGhost VPN is also an effective web browser extension that conceals IP addresses. This Firefox extension helps individuals to encrypt website traffic. CyberGhost VPN is a free-to-use platform that hides users’ IP addresses, enabling individuals worldwide to use the internet even within jurisdictions that restrict internet use. Individuals can fake IP addresses on this browser by clicking the power button.
Individuals can also try using IPBurger Proxy and VPN to preserve online anonymity. IPBurger Proxy and VPN is an extension on Firefox that enables user IP address protection. The extension can spoof a browser’s timezone by matching the time with the assigned IP address time. IPBurger Proxy and VPN also spoofs the GPS and languages of a user’s browser by matching with the assigned IP location factors, hiding the real ones.
Browse VPN is another Firefox extension that helps users change their IP addresses whenever wanted. This extension shields users’ real IP addresses, enabling access to geographically restricted content.
Can you get a Fake IP Address on Mobile Devices?
Yes, individuals can use fake IP addresses on mobile devices, whether android or iOs. Spoofing users’ locations is very important to maintain online privacy and access geographically restricted services. Changing a user’s mobile phone IP address is pretty simple and can be achieved by using VPNs, web proxies or Tor browser.
What are the Benefits of Using a Fake IP Address?
Fake IP addresses have many benefits for users, as detailed below.
- Keeping an individual’s online activity private: Each device that an internet user connects to the web has an IP address certain parties like the government can trace back to the owner. If one doesn’t want to be put under online scrutiny by the government, using a fake IP address could be a good option.
- Preventing tracking of users’ online footprints: Individuals can mask online activity from internet service providers via fake IP addresses. Individuals may be uncomfortable to learn that ISPs track online activity down to the last detail. Hiding a device’s IP addresses limits what the ISP can see to just an individual network connection to the service.
- Maintaining the confidentiality of sensitive online research: Working in a certain profession like top-secret government organizations means individuals conduct lots of research on sensitive issues. Leaking this information to the general public may put the individual at risk, hence the need to maintain the sensitive research confidential. Fake IP addresses mask this information and hide the researcher’s identity.
- Accessing geo-restricted content: The fake IP address will mimic the location where the content is available. One will easily stream and download whatever content wanted without hassles, making this one of the main fake IP address benefits.
- Surpassing restrictive government regulations: Some governments block citizens from using some internet services. Governments may also censor some content from reaching citizens for various reasons. However, citizens within these jurisdictions can bypass these restrictions and access whatever content is wanted. Citizens can do this by hiding IP addresses to maintain browsing activity discreetly.
Can a Fake IP Change Your Location?
Yes, a fake IP address can insinuate that one is in a different geographical location. Individuals can use Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to change locations to whatever country wanted. When connecting to a server in a different region, the IP address changes, concealing actual whereabouts. Some gamers who want to remain anonymous while playing online games like Hypixel can use a fake Hypixel server IP. Find out how to change IP address to another country via VPN on any search engine, and receive detailed instructions.
Can You Unblock Sites by Using a Fake IP Address?

Yes, if users wonder how to unblock sites, this can be done by using a fake IP address. For instance, a user can use a VPN to unblock sites. VPNs enable users to get a fake link to get IP addresses, concealing the actual location. Therefore, users can access the blocked websites without ISPs finding out. This is because VPNs act as an intermediary that enables individuals to access websites via the VPNs’ servers.
Apart from VPNs, individuals can unblock sites through open proxies. Open proxies help individuals quickly unblock web pages on public computers. Proxies hide users’ real identities from the page and conceal IP addresses from being tracked down.
Installing a proxy or VPN extension on browsers also helps individuals access blocked content. These extensions can help the users unblock powerful sites like Twitter, Amazon and YouTube. The extensions also enable individuals to choose different servers.
The Onion Routing (Tor) browser is another effective tool that conceals users’ IP addresses. The browser sends users’ data via a system of volunteer servers to hide an individual’s IP address. Therefore, the real IP address of a user is not exposed when trying to unblock sites.
Which Devices can you use a Fake IP Address On?
Individuals can use fake Internet Protocol addresses on the following devices.
- Android
- iOS
- Windows
Can you Fake a Static IP Address?
Yes, anyone can fake a static IP address to prevent being tracked down. One can do this by using IP masking to change the IP address and location. However, it may not yield many benefits in the long run. For instance, using a fake Hypixel IP address means one cannot communicate with other gamers. There won’t be any dialogue within the Hypixel operations because any reply will go to the real owner of the IP address. If that person’s computer is on the line, any feedback one intended to receive will be discarded.

