
Table of Contents
1. Open Your Windows Security Settings
Windows Security is a built-in software program from Windows that functions as an antivirus security tool. Using the program provides protection from online threats that can damage the content of the computer and the user’s data. Also, updates are provided promptly to help users keep the device safe and malware-free. Additionally, Windows Security executes a routine for virus detection and other malware scans.
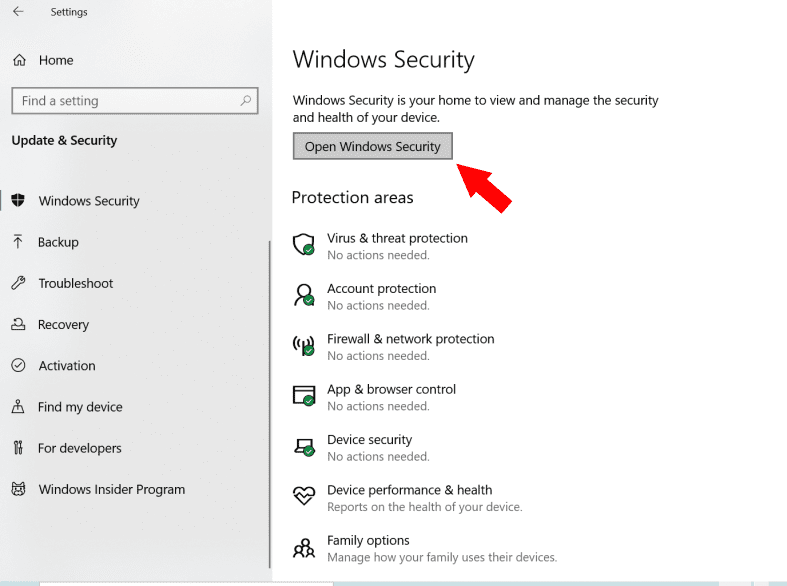
2. Select Virus & Threat Protection > Scan Options
Users can check the computer for any risk by navigating to the “Virus and Threat Protection” settings and then to the “Scan Options” menu. From there, users may perform various scans and view the outcome of prior scans. Virus and threat protection works by scanning the computer system for any malware and comparing the results to a global database of known cybersecurity threats.
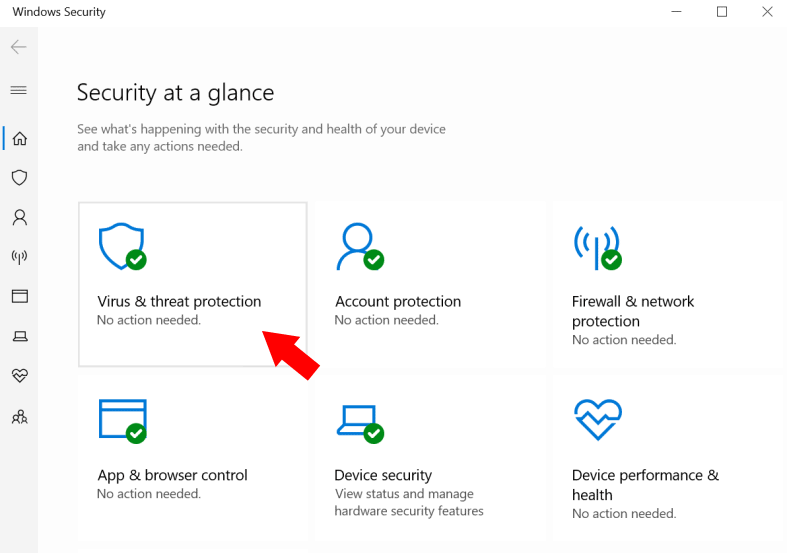
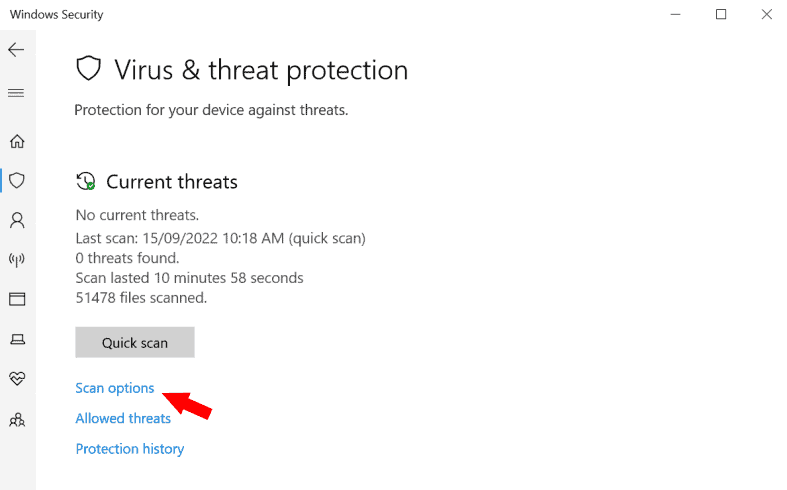
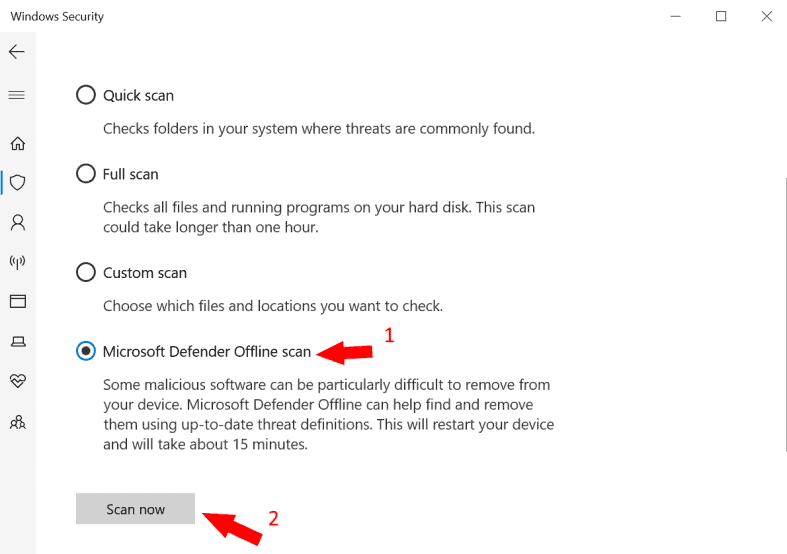
3. Select Windows Defender Offline Scan, and Then Select ‘Scan Now’
Windows Defender Offline is a Microsoft software program that facilitates the computer to boot and conduct a scan from a reliable setting. Scanning will only take about 15 minutes and will be restarted to refresh from any threats.
4. View the Results of Your Scan
Viewing the results of the scan can determine if the computer has any viruses, malware, spyware or other threats lurking in the system. The threats that have been detected will be erased from the computer system.
5. Open Your Windows Security Settings
As stated above, Window Security contains the essential instruments needed for scanning and removing computer malware. Open the Windows Security settings to run another scan or see past results.
6. Select Virus & Threat Protection > Protection History
The “Protection History” menu of Windows Security shows an index of current malware detections and details to help the user evaluate whether the danger has been addressed or removed.

What is Malware?
Malware is harmful software that infects computers/devices to collect users’ personal data and other information without consent. Every malware infection has a different attack strategy, ranging from covert to cunning. Additionally, even if malware can never harm the physical hardware of the computers, the viruses can and will hijack the core of computer operations. Malware can steal, encrypt or erase any data and spy on users’ behavior online without users’ consent or awareness. If users know how malware enters a system and operates, attacks can be prevented or mitigated. Moreover, antivirus and anti-malware software can help people identify and remove malicious files and programs.
How Can I Tell If My Computer is Infected with Malware?

There are multiple warning signs that a computer might be infected with malware. The foremost thing a user notices is when lots of pop-ups are revealed while working on the computer. The computer’s speed and performance will also diminish when corrupted. One of the negative impacts of malware is to delay the computer’s operating system, which can result in high resource usage. Additionally, computer systems collapse or freeze because of the malware inside the system. Users will also discover the consumption of disk space and loss of access to files, or worse, the whole computer system. The web browser settings can also be altered. Malware can attack any part of the computer system. Users must be cautious of any online activities or phishing emails/messages that will lead to infection.
Why Should You Remove Malware from Your Computer?
Removing malware will help mitigate any long-term damage to the computer system and prevent further data from being extracted. Victims of malware face consequences such as lost or permanently encrypted personal data, stolen bank account information, adjusted computer functions and online spying. Removing and preventing malware from returning will give the user the security of having a safe and protected computer. Users can also run antivirus software to avoid future malware-related threats, such as adware, spyware, ransomware and viruses.
What are the Most Effective Malware Removal Tools?

When a computer is infected with malware, users can utilize an effective malware removal tool to isolate and extract the malicious program. These tools can guarantee the simple and safe removal of viruses, spyware and Trojans. Users can also use the best malware removal tools to ensure that no personal information will be collected from malicious advertisements.
The most effective malware removal tools are listed below.
- Norton 360: Norton 360 can be used as both a VPN and a malware protection program. The Norton 360 has artificial intelligence that easily detects malware. The software will shield the user from anything that could harm the computer. Norton 360’s features include excellent malware protection, a secure VPN and a parental control system. Norton secures the VPN to avoid vulnerabilities to the system. Moreover, parental control is a great feature allowing limited access to the system to avoid infection.
- Kaspersky Antivirus: Kaspersky Antivirus is also an effective malware removal tool with plenty of features to boost users’ safety, including a high-quality antivirus scanner and other web security tools that can automatically catch the malware in the computer. Kaspersky is also quite simple to use, which is ideal for non-technical individuals.
- Malwarebytes Anti-Malware: Malwarebytes Anti-Malware offers a daily deep scan with updates, which also results in a very effective malware expulsion tool. The software also has anti-spyware and ad-blocking features, preventing pop-up advertisements that could contain malware. Along with these features, Malwarebytes can protect users’ identities, files and important documents from hackers and other third parties.
Does a VPN Protect You from Malware?
No, a VPN does not protect users from malware. Understanding why requires addressing the underlying question: What is a VPN? Virtual private networks (VPNs) are software programs that mainly work to cover users’ online activities and hide IP addresses from hackers, internet service providers, government surveillance agencies or other third-party actors. VPNs lack the capability to protect computers from malware. However, VPN users should be cautious about any online activities to prevent malware infection.

