Domain Name System (DNS) is an essential part of using the internet to the user’s advantage. The primary function of DNS is to convert a URL or the address that the user types into a website into an IP address. So a user can just enter google.com instead of having to remember to type a complex IP address like 172.217.1.46. But DNS has vulnerabilities, so users can use Private DNS. Private DNS is exclusive and has encrypted communication. And although there can be some technical difficulties, setting up a Private DNS is easy.
What Is Private DNS?
Most DNS servers are public, but there are some that are private and more secure. Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) are two protocols that encrypt DNS queries. Each has a DNS over the protocol, DoH is the DNS over HTTPS, and DoT is the DNS over TLS. All the user’s DNS requests are encrypted when using DNS over HTTPS or DNS over TLS. Nefarious parties will have far more difficulty spying on the network traffic with a private DNS.
Table of Contents
How Does Private DNS Work?
DoT and DoH are private, so the user can encrypt data to prevent eavesdropping by third parties. Attacks involving malware, ransomware and data theft frequently rely on DNS security flaws. The user needs to have a third-party DNS server with DoT or DoH capabilities and set up a DNS address on the device to enable private DNS.
How To Set Up a Private DNS on Windows?
Below are the steps to set up a private DNS on Windows.
- Open the “Settings.”
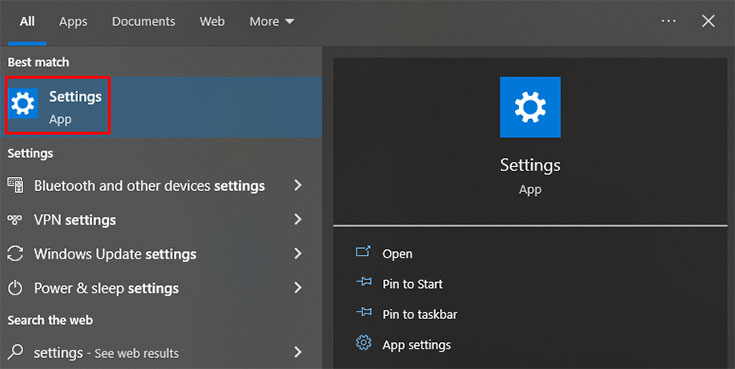
- Click on “Network & Internet.”
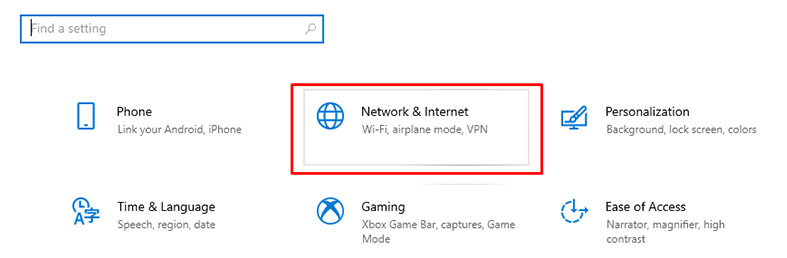
- On the “Advanced network settings,” click on “Network and Sharing Center.”
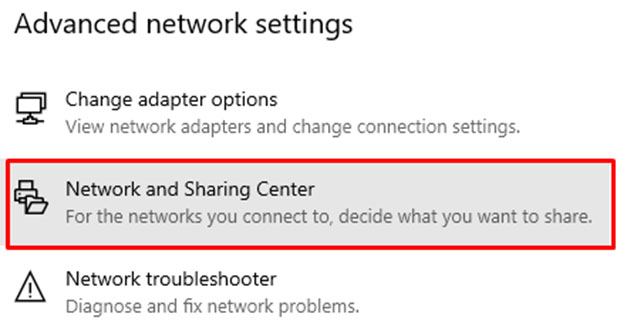
- “Change Adapter Settings” is on the left-hand side of the menu.
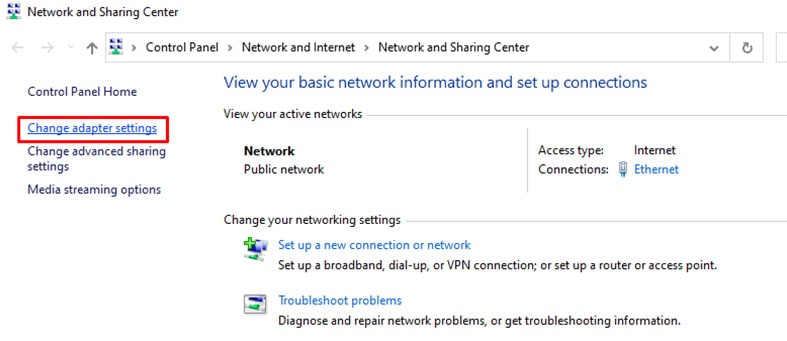
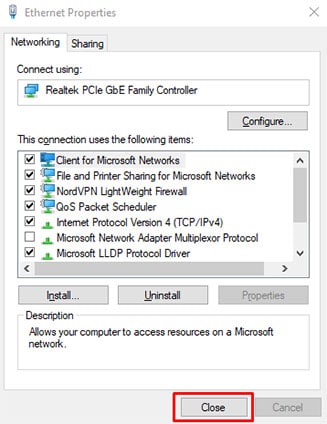
- Right-click the network the computer is connected to, then click on “Properties.”
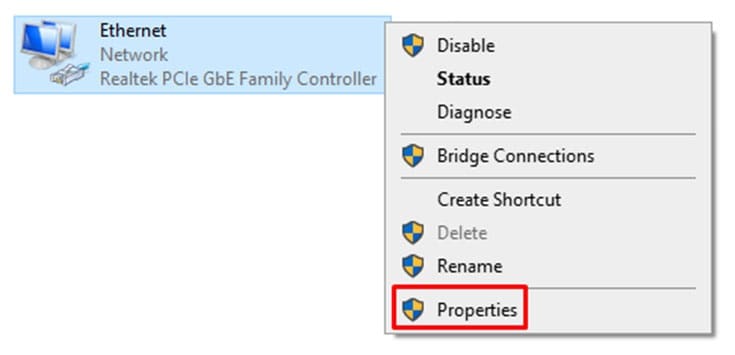
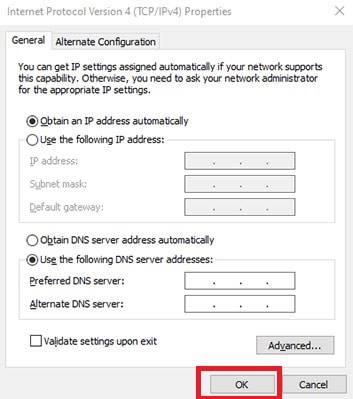
- From the list, click “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” and click on the “Properties” button on the lower right.
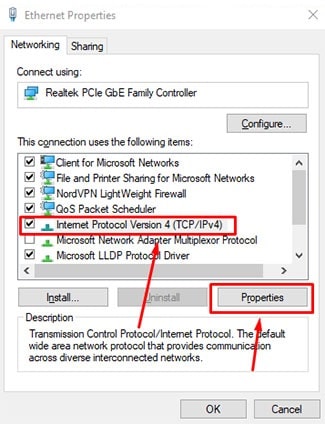
- Click on “Use the following DNS server addresses” and write the “Preferred DNS server.”
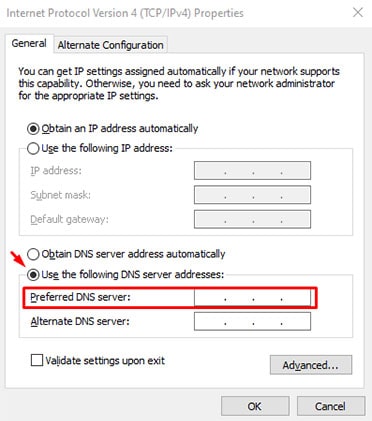
- Click on “OK” and Close.
How To Set Up a Private DNS on a Smartphone?
To enable the Private DNS, a user’s device must be running on Android 9.0 Pie or newer versions. The following steps can be followed to set up a private DNS on a smartphone.
- First, open “Settings.”
- Look for the section named “Connections.”
- Select “More Connection Settings” to expand the options.
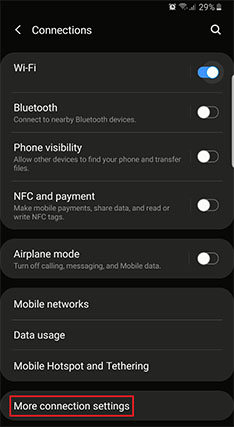
- Click on “Private DNS” under the network settings, though these vary on different android phones.
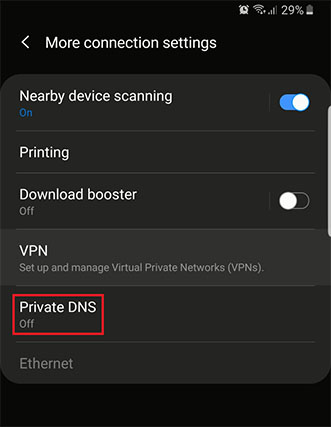
- Click “Private DNS provider hostname.”
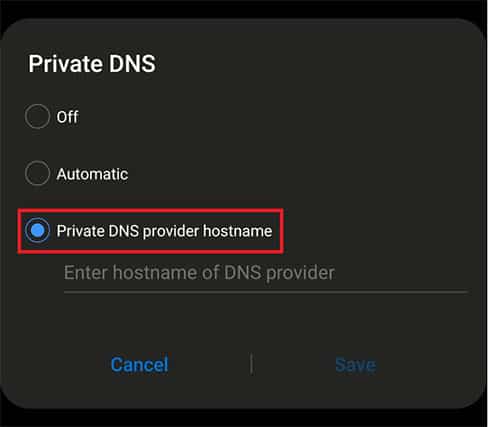
- Write the address of the preferred private DNS service.
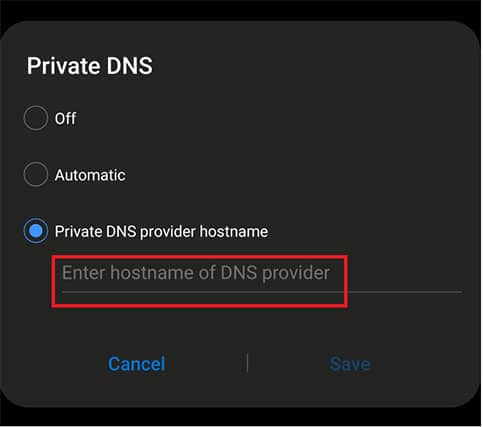
This is important:
Don’t forget to use the DNS server’s hostname, such as 1.1.1.1 or 8.8.8.8, rather than the IP address. Also, make sure the DNS server supports DNS over HTTPS and DNS over TLS.How To Set Up a Private DNS on an iPhone?
Listed below are the steps to set up a private DNS on an iPhone.
- Access “Settings.”
- Select “Wi-Fi.”
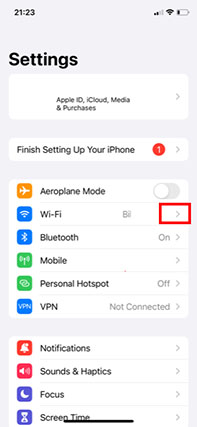
- To check the information about the Wi-Fi status, click the “i” indicator to see details.
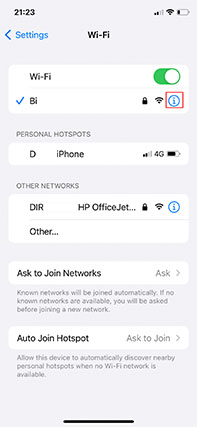
- Click on “Configure DNS” down below.
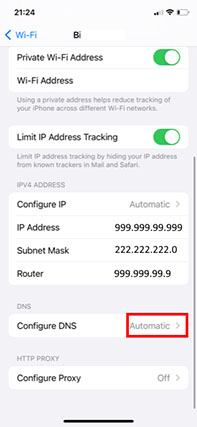
- Now, click on the setting and choose “Manual.”
- Click on “Add Server.”
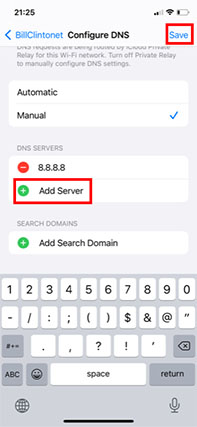
- Write the private DNS address.
How To Set Up a Private DNS on Mac?
On a Mac, setting up a private DNS has never been so simple. To set up a Private DNS on Mac, follow the steps below.
- Select the “Apple Menu.”
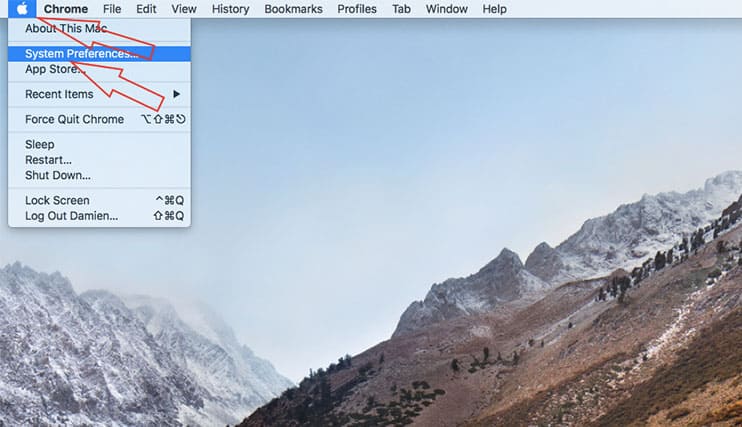
- Open “System Preferences.”
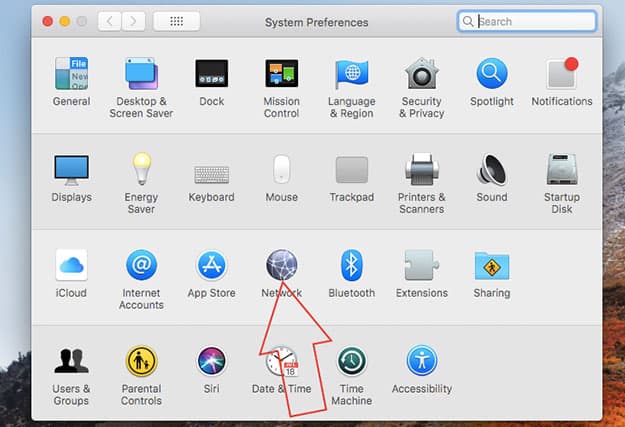
- Go to the “Network setting.”
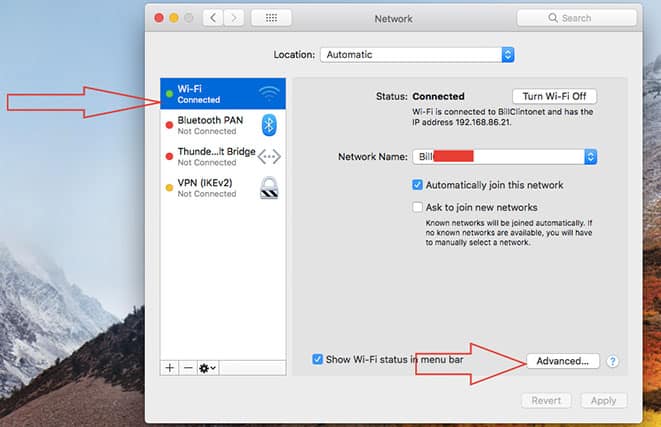
- Click on the network connection you are currently using and on “Advanced.”
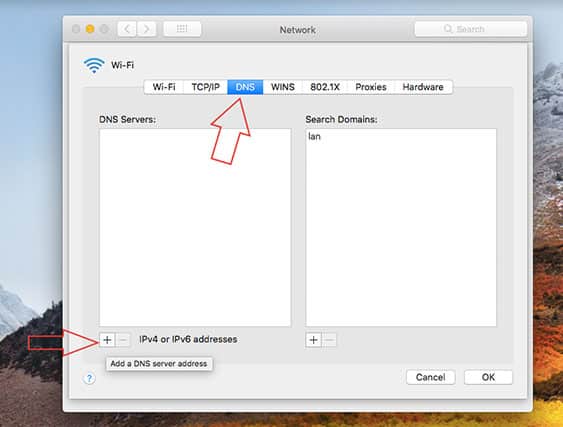
- Click on “DNS,” then select the add button (the plus symbol).
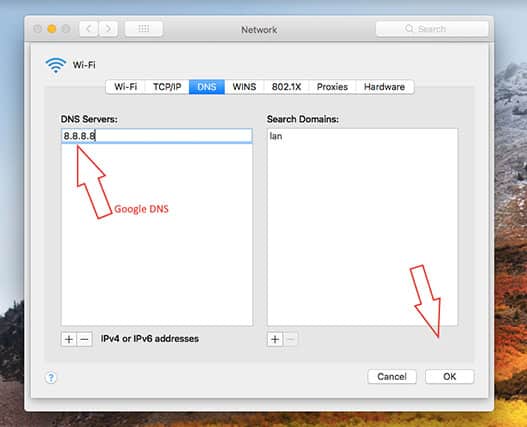
- Write the IPv4 or IPv6 address of the preferred DNS server.
- Select “OK.”
What Is the Benefit of Private DNS?
The main benefit of private DNS is the protection that private DNS offers for the user and the user’s devices from malicious actors on the internet. But even a private DNS may not be safe. When configuring a DNS address, check and validate the DNS to guarantee a safe connection.
Does a Private DNS Boost Internet Speed?
Yes, private DNS boosts internet speed. The reason behind a private DNS boosting the internet speed is the extra bandwidth. Private DNS improves internet speed into a fast and reliable one because private DNS has a minimum ping.
What Is the Best DNS Server?
Listed below is the top selection list of the Best DNS Servers of 2023.
- Constellix (Best Overall): Constellix is one DNS server that is run by the bigger company Tiggee LLC’s Anycast+ network. Each of the Constellix DNS servers is hosted within major data centers, allowing Constellix to have the best DNS servers. Constellix has provided unparalleled reliability in the industry because of the over 3,200 peers and a 540 Gbps peering capacity. Aside from proprietary DNS analytics programs, Constellix offers ultimate extensibility with a custom model.
- DNS Made Easy: DNS Made Easy’s goal is to give cutting-edge traffic management solutions to enterprises that need higher uptime, better performance and a reduction in workload and stress in the IT department. The biggest brands in the world have been able to succeed financially thanks to DNS Made Easy for over 20 years.
- Akamai: Akamai sustains and safeguards online life. Leading businesses all around the world select Akamai to create, distribute and secure respective digital experiences, assisting billions of people each day to work and play online. Customers can easily create and execute apps with the help of the most distributed computing platform in the world, which keeps user experiences close by and security concerns farther away.
What Are the Best Free DNS Servers?
Listed below is the top selection list of the best free DNS servers.
- Google Public DNS (Best Overall): Three main advantages are promised by Google Public DNS: a quicker surfing experience, enhanced security and precise results without redirecting. Google Public DNS is the best free DNS Server because Google Public DNS is operated by one of the largest IT companies, Google. But Google Public DNS only offers DNS resolution and caching, there is no site-blocking with Public DNS.
- OpenDNS: OpenDNS offers three main points: faster, more reliable home internet, safety, and easiness to set up. Every day, OpenDNS’ global network supports over 620 billion DNS queries, aside from over 60,000 new malevolent destinations including domains, URLs and IPs that are discovered every day. OpenDNS gives excellent performance while blocking over 7 million malicious sites and IPs.
- Quad9: The free service Quad9 takes the place of a company’s default DNS settings. Quad9 prevents the lookup of malicious hostnames from a current list of threats whenever your computer does any internet transactions that use the DNS. The blocking action ensures privacy while defending the computer and mobile device from a variety of dangers, like malware, botnets and spyware. Quad9 can also enhance and improve speed. Quad9’s goal is to give everyone access to a more secure and reliable internet.
Is Private DNS the Same as VPN?

No, Private DNS is not the same as VPN. The main difference between DNS and VPNs is privacy. People without a tech-background often use DNS and VPN interchangeably, which is totally wrong. Being private or public, subscription-based or free, DNS is a different term in IT from VPN. Using human-readable addresses, DNS is a standard mechanism that enables internet users to connect to websites. To get over censorship limitations brought on the DNS blocks, people modify and configure DNS. Obtaining a DNS enables a user to access websites that are not IP-level restricted. On the other hand, a user can view any websites and information using a VPN. Various features for privacy, speed and internet security are also included when using a VPN.
Note:
To reiterate the point on DNS vs. VPN, DNS works by converting domain names like HTTPS into IP addresses, which a user’s browser can then use to connect to a certain website. Internet Service Providers (ISP) can monitor online activities using DNS queries because most consumers use a default DNS that was provided by the ISP. But with the help of a Virtual Private Network (VPN), the communication between a user device and the internet is private. The user’s traffic is forwarded through a VPN server while the user’s IP address is changed. People use VPNs to avoid bandwidth throttling, get around geo-restrictions such as DNS and IP blocks, mask online identities and shield sensitive data from hackers and snoopers.Is Private DNS Safe?
Yes, Private DNS is safe. Private DNS is a safe browsing option that provides extensive access to a website that has been restricted and guards against online threats. There are no drawbacks to experimenting with Private DNS. A user’s operating system can be set up to use DNS over HTTPS or DNS over TLS. A user can always revert to the default or previous set-up if the new DNS servers turn out to be less reliable than the ones provided by the internet service provider. However, private DNS’s anonymity should compensate for the tiny speed difference.

